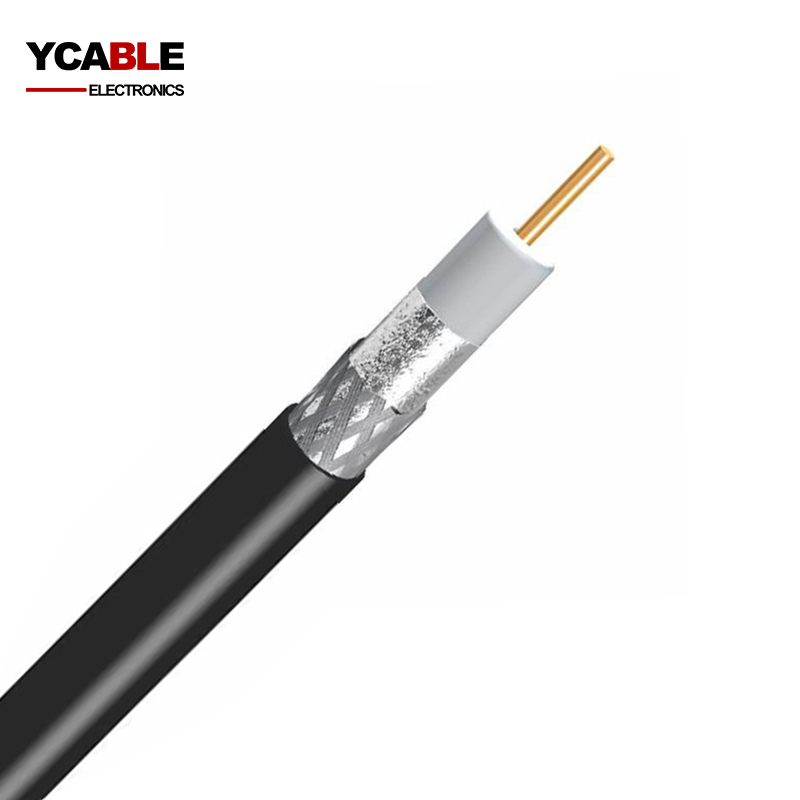
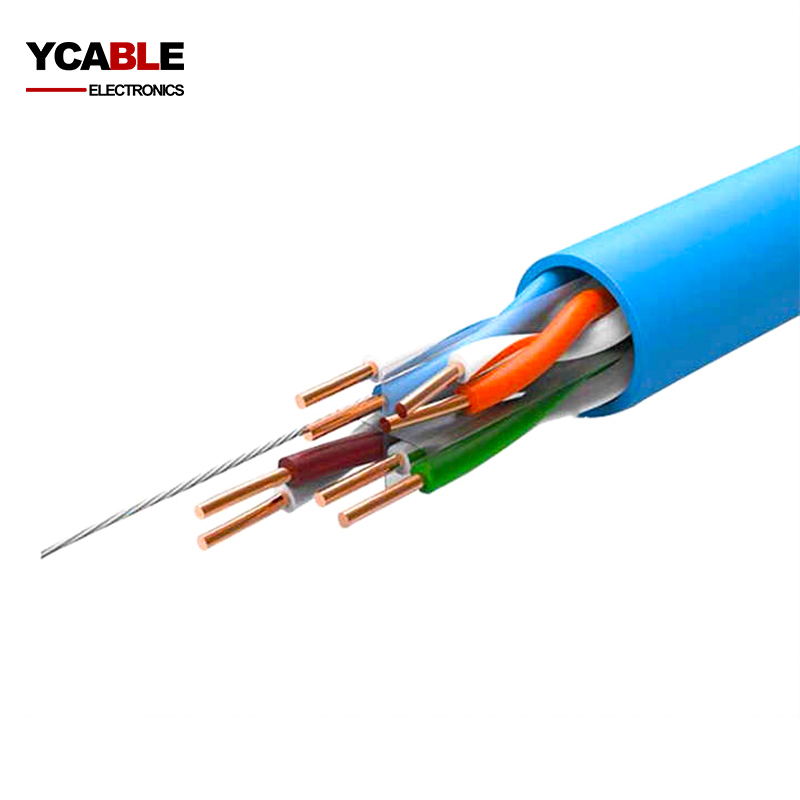
RG58 Coaxial Cable
RG58 Coaxial Cable
Item Number:RG58 Coaxial Cable
- Model: RG58 Coaxial Cable
- Size: 23AWG Solid or Stranded
- Color: White/Blue/Black/Gray/Custom
- Insulation: Foamed PE/Foamed Telflon
- Shield: Shield
- Jacket: PVC/LSZH/PE/Teflon
- Packing: 305M(1000FT)/CTN
- OD: 6.5mm/Custom
- Conductor Material: Bare Copper or CCS
- Drain wire: None
Environmental Specifications:
Environmental Space – Non-plenum
Flame Test Method – CMR
Installation Temperature – 0 °C to +60 °C (+32 °F to +140 °F)
Operating Temperature – -20 °C to +60 °C (-4 °F to +140 °F)
Temperature Rating – 75 °C
General Specifications:
Cable Type
RG58 Coaxial Cable
Conductor, quantity
1
Cable Component Type
PE, PVC, Horizontal
Conductor Gauge, singles
23AWG
Conductor Type, singles
Solid/Stranded
Characteristics:
- Impedance: 50 ohms (ideal for RF applications).
- Frequency Range: Typically up to 1 GHz (higher frequencies cause more signal loss).
- Center Conductor:
- CCS (Copper-Clad Steel): More durable but higher loss.
- Solid Copper: Better conductivity, lower loss.
- Shielding: Braided copper or aluminum for moderate interference protection.
- Dielectric: Polyethylene (PE) insulation.
- Outer Diameter: ~4.95 mm (thin and flexible).
- Attenuation: Higher than RG8 or RG213, limiting long-distance performance.
- Power Handling: Lower compared to thicker 50-ohm cables.
In general, RG58 is a 50-ohm coaxial cable commonly used for RF communication, low-power signal transmission, and testing applications.


Categories
RG58 Coaxial Cable
| Electrical Specifications | |
| ITEM | RG58 Coaxial Cable |
| dc Resistance Unbalance, maximum | 5 % |
| dc Resistance, maximum | 7.61 ohms/100 m |
| Mutual Capacitance | 5.6 nF/100 m @ 1 kHz |
| Nominal Velocity of Propagation (NVP) | 69 % |
| Operating Frequency, maximum | 300 MHz |
| Operating Voltage, maximum | 80 V |
| Transmission Standards | ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 CENELEC EN 50288-6-1 ISO/IEC 11801 Class E |
| Dielectric Strength, minimum | 1500 Vac 2500 Vdc |
Description
What is RG58 cable?
RG58 is a coaxial cable commonly used for radio frequency (RF) communications, low-power signal transmission, and data applications. It has a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms, making it suitable for applications such as:
- RF Communications: Connects CB radios, ham radios, and RF transmitters.
- Antenna Connections: Links antennas to radio equipment.
- Networking (Legacy): Used in older 10BASE2 Ethernet (Thinnet) networks.
- Test Equipment: Connects oscilloscopes, signal generators, and other lab devices.
- Surveillance Systems: Sometimes used for analog CCTV setups.
RG58 typically consists of a stranded or solid center conductor, a dielectric insulator, a shielding layer (braid or foil), and an outer protective jacket. It is flexible and relatively low-cost but has higher signal loss compared to thicker coaxial cables like RG8.
What is CCS RG58 cable?
CCS RG58 refers to RG58 coaxial cable with a Copper-Clad Steel (CCS) center conductor. This means the core is made of steel with a thin layer of copper.
Characteristics of CCS RG58:
- Higher Strength: More durable and resistant to breaking.
- Lower Cost: Cheaper than solid copper versions.
- Higher Signal Loss: Higher resistance than pure copper, leading to more attenuation, especially at high frequencies.
- Still Supports RF Applications: Suitable for applications where flexibility and low cost are prioritized over minimal signal loss.
Best Uses:
- Short-distance RF communication (CB radios, antennas).
- Cost-sensitive applications where minimal power loss is acceptable.
- General-purpose signal transmission with moderate performance needs.
For applications requiring better conductivity and lower loss, pure copper RG58 (BC or SCC) is preferred.
The difference between CCS RG58 and copper RG58 cable
The main difference between CCS RG58 (Copper-Clad Steel) and Copper RG58 lies in the conductor material, affecting electrical performance and cost
| Feature | CCS RG58 (Copper-Clad Steel) | Copper RG58 (Bare Copper - BC) |
| Center Conductor | Steel core with a thin copper coating | Pure copper |
| Conductivity | Lower (higher resistance) | Higher (better signal transmission) |
| Signal Loss | Higher attenuation, especially at high frequencies | Lower attenuation, better performance |
| Strength & Durability | More rigid and durable | More flexible but less strong |
| Cost | Cheaper | More expensive |
| Best For | Short cable runs, budget applications | High-performance RF, low-loss applications |
Which One to Choose?
- Use CCS RG58 for cost-sensitive applications where some signal loss is acceptable (e.g., CB radios, general RF use).
- Use Copper RG58 when better signal quality and lower loss are needed (e.g., longer cable runs, sensitive RF applications).
custom RG58 cable and custom Semi-finished coaxial RG cable
Custom RG58 Cable:
- Made to specific lengths, connectors, and shielding types based on user needs.
- Can include pure copper or CCS conductor, different jacket materials (PVC, LSZH, etc.), and custom impedance matching.
- Used for RF applications, antennas, network setups, and lab equipment.
Custom Semi-Finished Coaxial Cable:
- Partially manufactured coaxial cables, allowing customization before final assembly.
- Comes with unfinished ends, allowing users to add their own connectors, shielding, or jacket.
- Ideal for manufacturers, integrators, and projects requiring specific performance tuning.
Would you like recommendations on suppliers or manufacturing specifications?