Custom Underground Tracer Wire Manufacturer In China
What Is Tracer Wire and What Is It For?
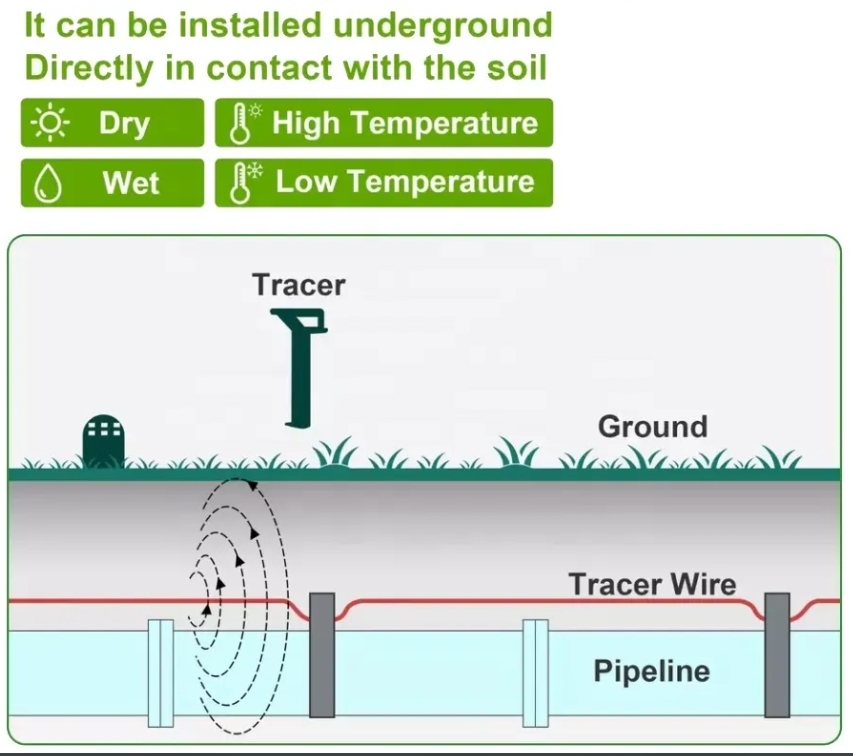
Tracer wire, also called locating or locator wire, is a single conductor wire installed alongside underground pipes or utilities during installation. It allows workers to locate these buried assets later. Tracer wire can be made of copper, copper-clad steel, or stainless steel and is insulated with various materials.
How It Works:
- Tracer wire is laid along the length of a pipe or conduit and buried.
- Each end of the wire is connected to a grounded point, creating a grounded system.
- Crews use a wire tracer, an above-ground device emitting a low-frequency signal, to locate the wire without energizing it.
Purpose:
Tracer wire helps locate underground utilities accurately, reducing the risk of damage during repairs or new installations. It is a cost-effective way to prevent costly mistakes.
Why we need practical tracer wires?
Using tracer wire matters because it ensures the accurate location of underground utilities, reducing the risk of dangerous and costly accidents during digging or maintenance. Without knowing the location of these utilities, crews could inadvertently cut through lines, causing:
- Safety Risks: Striking gas or electric lines can lead to explosions or severe injuries.
- Service Disruptions: Damaging telecom or water lines can inconvenience homeowners and businesses.
Benefits of Using Tracer Wire:
- Safety: Helps prevent accidents during excavation by identifying utility locations.
- Efficiency: Saves time when locating assets for maintenance or repairs.
- Accuracy: Enables precise digging, reducing unnecessary excavation.
- Compliance: Supports future technologies like utility mapping.
Applications:
- Tracer wire is used in utilities such as water, gas, sewer, fiber optics, and irrigation systems. The color coding, defined by the American Public Works Association (APWA), further enhances safety by identifying specific utility types (e.g., blue for potable water, yellow for gas).
The difference between tracer wire and THHN wire
Tracer Wire Benefits:
- Designed for Underground Use: Tracer wire is specifically built to endure the environmental conditions of underground applications, including moisture, soil chemicals, and physical stress.
- It typically has a robust polyethylene or other durable insulation designed for direct burial.
- Flexibility in Length and Connectivity: Tracer wire systems include grounding connections and splicing accessories for long runs, ensuring effective signal continuity.
- Signal Transmission: Tracer wire is optimized for use with locating equipment, emitting signals for precise underground utility detection.
- Color Coding: Tracer wire follows APWA standards, with color-coded insulation to identify specific utilities, reducing the risk of errors during excavation.
- Durability: Options like copper-clad steel (CCS) provide high tensile strength, making it more resistant to breakage than some alternatives.
THHN Wire Limitations:
- Not Designed for Underground Use: THHN is primarily intended for indoor or conduit applications. Its insulation is not rated for direct burial without additional protective measures, making it vulnerable to moisture and environmental degradation.
- Incompatible with Locator Equipment: THHN lacks the properties to work effectively with locating devices, limiting its use in applications where utility location is critical.
- Limited Insulation Durability: Nylon-coated insulation on THHN wire may degrade faster in soil, requiring additional protection to match the longevity of tracer wire.
Key Takeaway:
Tracer wire is the better choice for underground applications, ensuring durability, signal transmission, and compliance with utility location standards. THHN is suitable for indoor or conduit-based applications but lacks the robustness and functionality required for buried utilities.

What gauge does tracer wire need to be?
The appropriate gauge for tracer wire depends on the application and the utility it is marking, but common practices are:
- 14 GA tracer wire: Used in conjunction with a signal transmitter and receiver for detecting and mapping buried utilities without excavation.
- 12 AWG tracer wire: Suitable for standard utility applications such as water, sewer, and gas lines in shorter runs.
- 10 AWG tracer wire: Recommended for longer runs or when more signal strength is required for locating, often used in gas or directional drilling applications.
- 8 AWG tracer wire or Thicker: Used for very long runs, deep installations, or projects with high signal requirements, such as pipelines or major utility projects.
Factors Influencing Gauge Selection:
- Distance: Thicker wire (lower gauge) is better for maintaining signal strength over long distances.
- Application: Larger gauges may be specified for critical utilities like gas pipelines or directional drilling projects.
- Soil Conditions: In areas with high interference or challenging conditions, a thicker gauge ensures better signal transmission.
Always consult local regulations or project specifications for the exact requirements.










