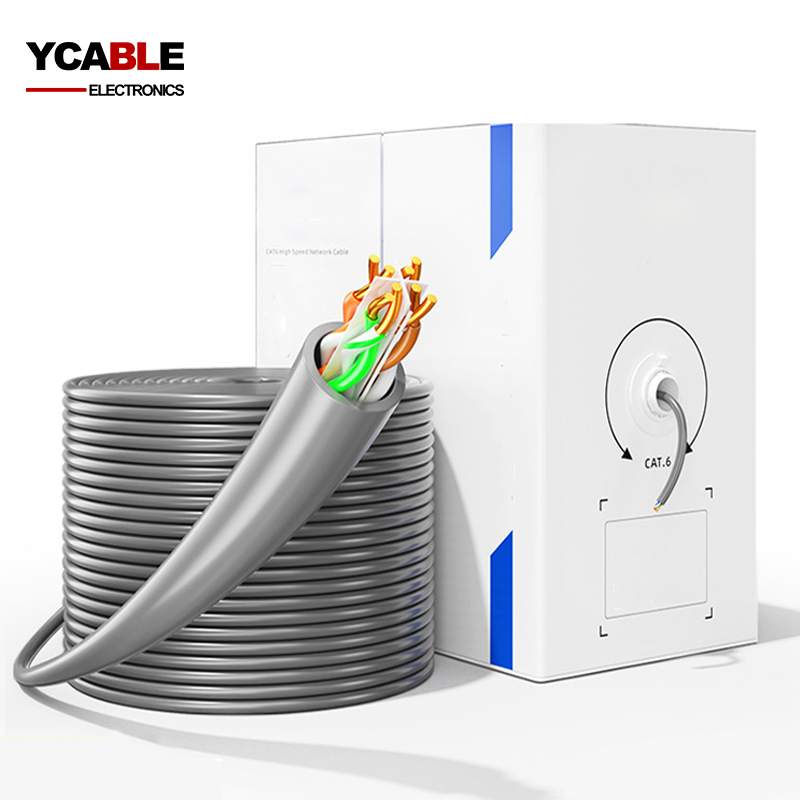
CCA Ethernet Cable UTP CAT6
CCA Ethernet Cable UTP CAT6
Item Number:CCA Cat6 UTP
- Model: CCA CAT6 UTP LAN CABLE
- Size: 23AWG Solid or Stranded
- Color: White/Blue/Black/Gray/Custom
- Insulation: PE
- Shield: Unshielded
- Jacket: PVC/LSOH/Custom
- Packing: 30.5M(100FT), 305M(1000FT)/CTN/Custom
- OD: 5.9mm/Custom
- Conductor Material: Bare Copper or CCA
- Drain wire: None
Environmental Specifications:
Environmental Space – Non-plenum
Flame Test Method – CMR
Installation Temperature – 0 °C to +60 °C (+32 °F to +140 °F)
Operating Temperature – -20 °C to +60 °C (-4 °F to +140 °F)
Temperature Rating – 75 °C
General Specifications:
Cable Type
U/UTP (unshielded)
Pairs, quantity
4
Cable Component Type
Horizontal
Conductor Gauge, singles
23AWG
Conductor Type, singles
Solid/Stranded
Characteristics:
- Performance up to 250-300 MHz, CAT5E is only 100 MHz.Suitable for 10GBASE-T
- Enhanced protection against crosstalk and system noise.
- There are many brands sold on the market, so everyone must choose a large brand to ensure the quality of the network cable.
- Suitable for indoor applications
In general, CCA CAT6 UTP can stably support gigabit networks without being stuck or disconnected, and its performance is far higher than that of CCA CAT5E UTP. I suggest you choose the CCA CAT6 UTP network cable.
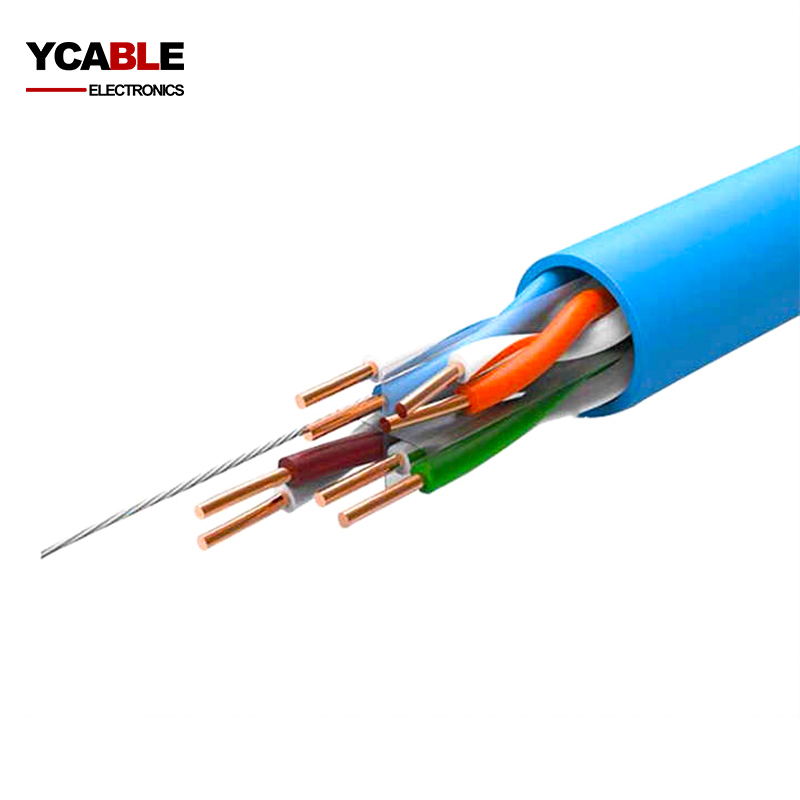

Categories
CCA Category 6 U/UTP Cable
| Electrical Specifications | |
| ANSI/TIA Category | 6 |
| dc Resistance Unbalance, maximum | 5 % |
| dc Resistance, maximum | 7.61 ohms/100 m |
| Mutual Capacitance | 5.6 nF/100 m @ 1 kHz |
| Nominal Velocity of Propagation (NVP) | 69 % |
| Operating Frequency, maximum | 300 MHz |
| Operating Voltage, maximum | 80 V |
| Transmission Standards | ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 CENELEC EN 50288-6-1 ISO/IEC 11801 Class E |
| Dielectric Strength, minimum | 1500 Vac 2500 Vdc |
Description
What is CCA UTP cable?
CAT6 UTP CCA cables, crafted with Copper-Clad Aluminum conductors, feature typically 4 twisted pairs encased in either PVC or LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) jackets. These cat6 CCA cables, developed by cat6 cca cable manufacturers, present a budget-friendly option for fundamental networking necessities. This is particularly relevant in scenarios where financial considerations are paramount and the required cable length remains within modest bounds. Despite their cost benefits, it's prudent to acknowledge the inherent constraints of CAT6 CCA, notably in aspects of endurance and efficacy over extended distances.
Advantages for CCA CAT6 Cable
- Economic Viability: The incorporation of aluminum, a material less costly than copper, renders CAT6 CCA an attractive, cost-efficient alternative for companies intent on enlarging or enhancing their network framework without significant financial burden.
- Operational Efficiency: Although CAT6 CCA does not match the conductivity level of pure copper cables, it reliably delivers competent performance for a plethora of commercial uses. It capably supports brisk data transmission speeds reaching 1 Gbps, aligning well with the demands of numerous office setups.
- Ease of Installation and Portability: The lightweight nature of CAT6 CCA cables, owing to their aluminum content, surpasses the heft of solid copper variants. This attribute simplifies the installation process, particularly in intricate network configurations, offering greater flexibility and ease of handling.
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
CCA Cat6 vs copper
Performance Variations Between CAT6 CCA and Solid Copper Cables
In the realm of network cabling, a distinct performance disparity exists between CAT6 UTP CCA cables and solid copper cables. Solid copper cables stand as the quintessential choice for Power over Ethernet (PoE) and rapid Ethernet applications, making them a prime selection for data centers and businesses prioritizing maximal speed. Conversely, CAT6 CCA cables, which are a product of copper-clad aluminum technology, are more suited for elementary networking tasks. For more sophisticated network requirements, an upgrade to pure copper cables is often necessitated.
Cost Disparities Between the Two Cable Types
There's a noticeable price gap when comparing these two types of cables. Pure copper cables, a preference among cat6 cca cable manufacturers, tend to be pricier, a direct consequence of copper being a more expensive material. This higher cost is a trade-off for acquiring the superior qualities of pure copper. In contrast, CAT6 UTP CCA cables, characterized by their copper-clad aluminum composition, are more budget-friendly.
Connectivity and Safety Compliance
When it comes to adherence to safety standards, not all UTP cables are equal. Pure copper cables are often recommended for installations in environments where safety is a critical concern, as they generally meet a broader range of safety standards. This is due to their 100% pure copper composition. On the other hand, CAT6 CCA cables may not fulfill all safety benchmarks, given their copper-clad aluminum makeup. This factor becomes crucial in decisions about cable selection, particularly in settings where compliance and safety are paramount.
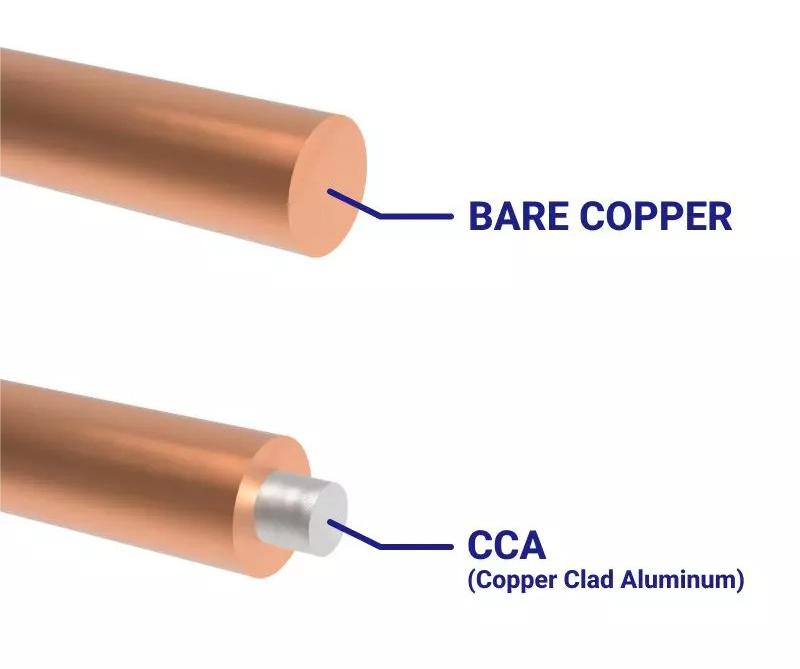
How do I know if my CAT6 is CCA?
- Weight Comparison Test: When evaluating the weight of different cable types, it's notable that the density of aluminum or steel is considerably lower than that of copper. As a result, a CAT6 UTP CCA cable, which uses either Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA) or Copper-Clad Steel (CCS) conductors, will be significantly lighter than its copper counterpart for the same length. To ensure accuracy in this assessment, it's essential to remove the cable from any additional packaging materials, as some cat6 cca cable manufacturers may use heavier packaging elements.
- Conductor Identification Test: To determine the material of the conductor in a cable, start by removing the outer jackets. If the exposed conductor displays an orange hue, it indicates a copper top layer. Proceed to strip the conductor further using a utility knife. Should the color beneath be silver, this reveals the presence of either aluminum or iron, indicating a CCA or CCS conductor coated with a copper layer.
- Flexibility and Durability Test: For this test, isolate the wires and strip the conductors. Then, repeatedly twist the bare conductor with your fingers. A CAT6 CCA or CCS conductor tends to break more rapidly compared to a solid copper conductor, highlighting a difference in flexibility and durability.
- Flame Resistance Test: To conduct this test, strip the cable sheath to expose the conductor. Apply a flame, such as from a lighter, to the conductor. A CCA or CCS conductor will typically melt and detach quickly under these conditions, unlike a pure copper conductor.
- Electrical Performance Test: Utilize a copper certification device to evaluate the cable's performance. For CAT6 UTP CCA or CCS cables, the DC resistance unbalance value is likely to be outside the specified range. To ensure accurate testing, adhere to the ISO/IEC 11801 standard. This is crucial because, while ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 sets this parameter for channels, ISO/IEC 11801 establishes it for both permanent links and channels.

Related Products
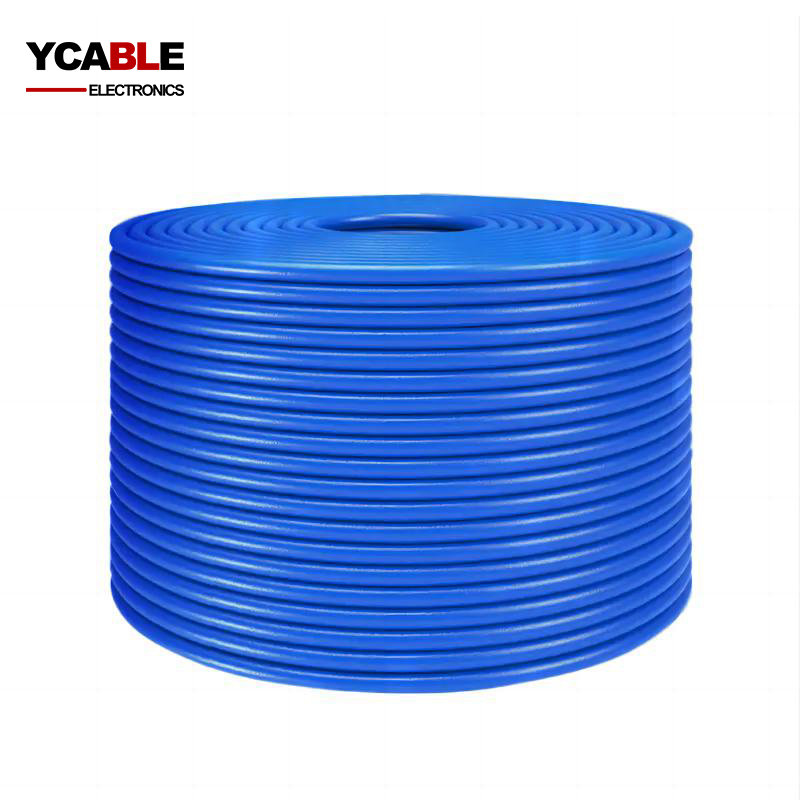

CAT6 wire FTP LAN cable
200FT CAT6 FTP cable shielded ethernet network LAN cable manufacturer in China
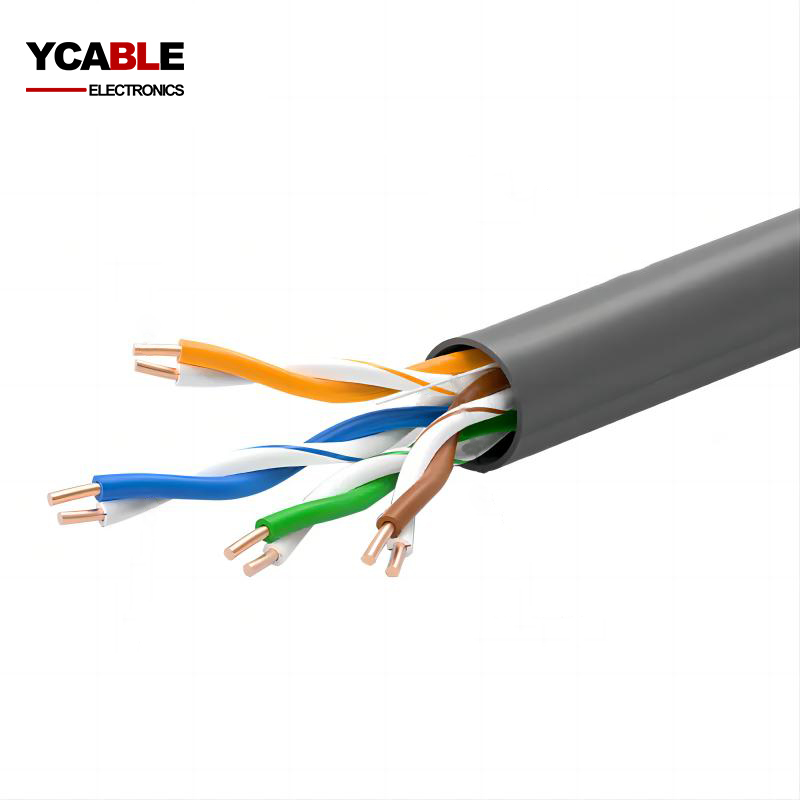

CCA Ethernet Cable UTP CAT5E
CCA Ethernet Cable CAT5E UTP 4pair 24awg 4x24AWG network cable Lan Cable ...
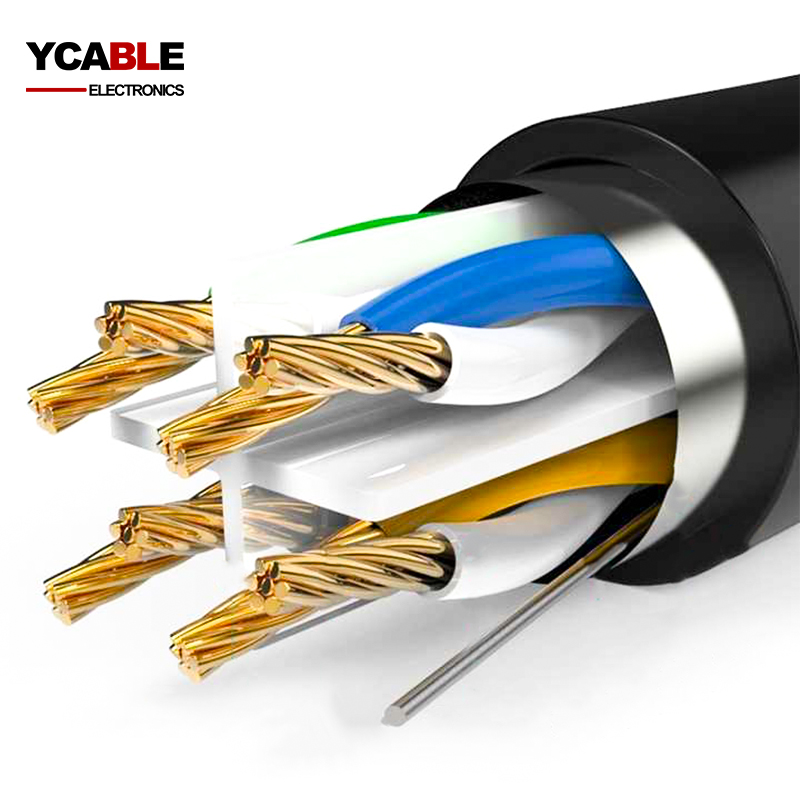

CCA Ethernet Cable FTP CAT6
CCA Ethernet Cable CAT6 U FTP Al-Foil shielded weatherproof bulk network cable ...









