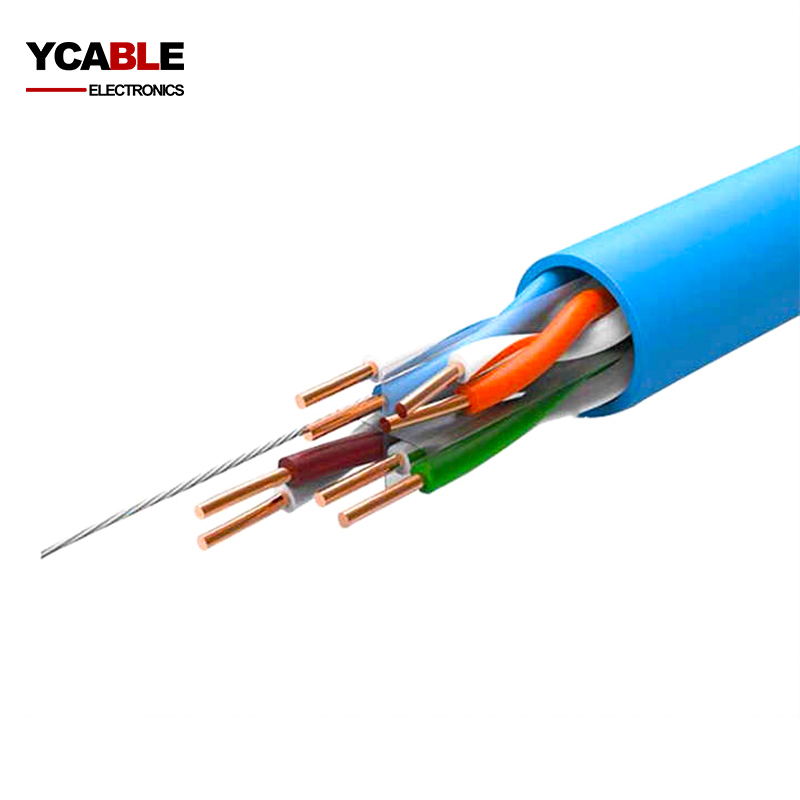
CAT6 wire UTP LAN cable
CAT6 wire UTP LAN cable
Item Number:Cat6 UTP
- Model: CAT6 UTP LAN CABLE
- Size: 23AWG Solid or Stranded
- Color: White/Blue/Black/Gray/Custom
- Insulation: PE
- Shield: Unshielded
- Jacket: PVC/LSOH
- Packing: 30.5M(100FT), 305M(1000FT)/CTN
- OD: 5.9mm
- Conductor Material: Bare Copper or CCA
- Drain wire: None
Environmental Specifications:
Environmental Space – Non-plenum
Flame Test Method – CMR
Installation Temperature – 0 °C to +60 °C (+32 °F to +140 °F)
Operating Temperature – -20 °C to +60 °C (-4 °F to +140 °F)
Temperature Rating – 75 °C
General Specifications:
Cable Type
U/UTP (unshielded)
Pairs, quantity
4
Cable Component Type
Horizontal
Conductor Gauge, singles
23AWG
Conductor Type, singles
Solid/Stranded
Characteristics:
- Performance up to 250-300 MHz, CAT5E is only 100 MHz.Suitable for 10GBASE-T
- Enhanced protection against crosstalk and system noise.
- There are many brands sold on the market, so everyone must choose a large brand to ensure the quality of the network cable.
- Suitable for indoor applications
In general, CAT6 UTP can stably support gigabit networks without being stuck or disconnected, and its performance is far higher than that of CAT5E UTP. I suggest you choose the CAT6 UTP network cable.


Categories
Category 6 U/UTP Cable
| Electrical Specifications | |
| ANSI/TIA Category | 6 |
| dc Resistance Unbalance, maximum | 5 % |
| dc Resistance, maximum | 7.61 ohms/100 m |
| Mutual Capacitance | 5.6 nF/100 m @ 1 kHz |
| Nominal Velocity of Propagation (NVP) | 69 % |
| Operating Frequency, maximum | 300 MHz |
| Operating Voltage, maximum | 80 V |
| Transmission Standards | ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 CENELEC EN 50288-6-1 ISO/IEC 11801 Class E |
| Dielectric Strength, minimum | 1500 Vac 2500 Vdc |
Description
What is UTP with Cat6?
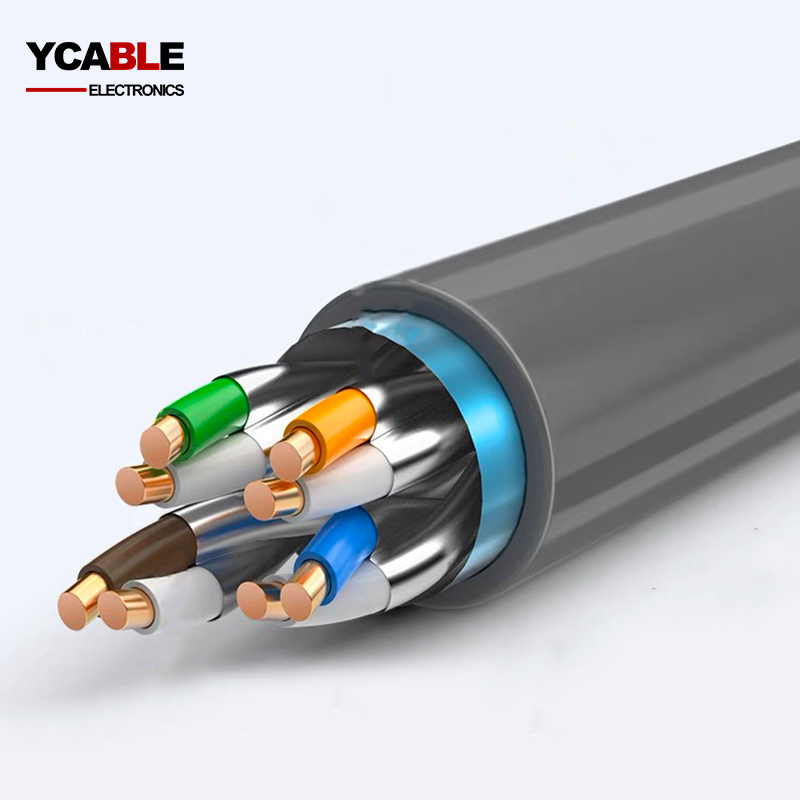
Category 6, widely recognized in the IT realm as a network, LAN, or Ethernet data cable, is a 4 twisted pair cable made of sheathed copper wire. It's known for its capacity to support data transfer rates reaching up to 1 gigabit (1,000 megabits). This enhanced bandwidth capability is crucial for the swift transmission of substantial files across office networks.
CAT6 UTP cables, a staple product for many CAT6 UTP cable manufacturers, are engineered to facilitate Gigabit Ethernet data rates at a swift pace of 1 gigabit per second. Notably, these cables can support 10 Gigabit Ethernet connections across limited stretches—typically up to around 180 feet for a single cable. A defining feature of the Cat6 cable is its composition, which includes four pairs of copper wire. All these pairs are actively used in signaling, contributing to the cable's high-performance profile.
This cable is notably versatile, showing compatibility with various Ethernet standards including fast Ethernet 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and Gigabit networks. Moreover, its design ensures backward compatibility with older versions like Cat5/5E and Cat3.
At each end of a CAT6 UTP cable, there's commonly an eight-position eight connector (8P8C), better known as the RJ45 jack. This connector plays a pivotal role in linking two devices via the Cat6 cable. To harness the full potential of the cable's performance, it's essential to use jacks that align with the Cat6 rating.

| Product Construction | |||||
| Conductor | Material | Pure copper | |||
| AWG | 23 | ||||
| Diameter(mm) | 0.57 | ||||
| Insulation | Material | PE | |||
| Average Thickness(mm) | 0.24 | ||||
| Minimum Thickness(mm) | 0.21 | ||||
| Diameter(mm) | 1.02 | ||||
| pair Twist Diameter(mm) | 2.04 | ||||
| Seperator(mm) | w=4.5,h=0.5 | ||||
| Cable Diameter(mm) | 5.30 | ||||
| PEL(mm) | w=22,h=0.015 | ||||
| Rip-cord | 1*3D | ||||
| Jacket | Material | PE | |||
| Average Thickness(mm) | 0.58 | ||||
| Minimum Thickness(mm) | 0.53 | ||||
| Diameter(mm) | 6.50 | ||||
| Color | |||||
| Insulation Wire | Blue*White/Blue | Orange*White/Orange | |||
| Green*White/Green | Brown*White/Brown | ||||
| Jacket | Accoring to customer's requirement | ||||
what is the difference between CAT5e and CAT6 cable?
CAT5e vs. CAT6 Bandwidth Comparison
- Both CAT5e and CAT6 cables, commonly utilized in CAT6 UTP networks, are capable of handling speeds up to 1000 Mbps, or a Gigabit per second, which is typically more than enough for most internet connections. It's rare to find an internet connection exceeding 500 Mbps speed in typical settings.
- The primary distinction between CAT5e and CAT6, especially in products from reputable cat6 manufacturers, lies in their bandwidth capabilities. CAT6 cables, designed to operate at frequencies up to 250 MHz, surpass the 100 MHz capacity of CAT5e. This difference in frequency allows CAT6 cables to process more data simultaneously, akin to comparing a 2-lane to a 4-lane highway: both may allow the same speed, but the latter can handle more traffic at once.
Speed Capabilities: CAT5e vs. CAT6
- Due to the higher frequency performance of CAT6 cables, peaking at 250 MHz, they can support speeds up to 10GBASE-T or 10-Gigabit Ethernet. This is a significant leap from CAT5e cables, which max out at 1GBASE-T or 1-Gigabit Ethernet.
Crosstalk Considerations: CAT5e vs. CAT6
- Both CAT5e and CAT6 cables are composed of copper wires with 4 twisted pairs. Historically, CAT6 cables achieved their 250 MHz performance using a nylon spline to isolate twisted pairs, but modern CAT6 cables, being more flexible, employ alternative methods for noise reduction.
- CAT6, regardless of the spline, adheres to stricter standards for crosstalk and system noise. Compared to CAT5e, it significantly reduces interference or Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT), and also enhances Equal-Level Far-End Crosstalk (ELFEXT), Return Loss (RL), and Insertion Loss (IL). This results in diminished system noise, fewer transmission errors, and heightened data transmission rates.
Maximum Length Differences: CAT5e vs. CAT6
- Both CAT5e and CAT6 cables offer optimal performance up to 100 meters per network segment. Beyond this length, performance deteriorates. For 10GBASE-T applications, the maximum effective length of a CAT6 cable decreases to 55 meters, beyond which the speed reverts to 1GBASE-T. For full 100 meter 10GBASE-T performance, CAT6A or Augmented Category 6 cable is recommended.
Visual Distinctions: CAT5e vs. CAT6
- Usually, the cable category is printed on the cable itself. If not, it's difficult to differentiate based on color or RJ45 connectors. However, CAT6 cables are often thicker than CAT5e cables due to the use of thicker copper wires.
Cost Analysis: CAT5e vs. CAT6
- The price of Ethernet cables, including CAT6 UTP and CAT5e, is influenced by factors like length, quality, copper content, and manufacturer. Generally, CAT6 cables are priced about 10-20% higher than CAT5e cables.
| Electrical Characteristic | ||||||
| Impedance Ω | Propagation Delay Skew ns/100m | Capacitance Unbalance | Conductor Resistance@20℃ Ω/km | Umbalance Resistance % | ||
| 100±15 | <=45 | <=330 | <=9.5 | <=5 | ||
| Frequency MHZ | Return Loss >=dB | Attenuation <=dB/100m | Next >=dB/100m | PS Next >=dB/100m | Elfext >=dB/100m | PS Elfext >=dB/100m |
| 1 | 20.00 | 1.85 | 65.31 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 60.8 |
| 4 | 23.01 | 3.69 | 56.28 | 55.0 | 51.7 | 48.7 |
| 8 | 24.52 | 5.26 | 51.77 | 48.8 | 45.7 | 42.7 |
| 10 | 25.00 | 5.89 | 50.31 | 47.3 | 43.8 | 40.8 |
| 16 | 25.00 | 7.51 | 47.25 | 44.3 | 39.7 | 36.7 |
| 20 | 25.00 | 8.42 | 45.80 | 42.8 | 37.7 | 34.7 |
| 25 | 24.32 | 9.47 | 44.35 | 41.3 | 35.8 | 32.8 |
| 31.25 | 23.64 | 10.64 | 42.89 | 39.9 | 33.9 | 30.9 |
| 50 | 22.21 | 13.64 | 39.83 | 36.8 | 29.8 | 26.8 |
| 62.5 | 21.54 | 15.36 | 38.38 | 35.4 | 27.8 | 24.8 |
| 100 | 20.11 | 19.78 | 35.31 | 32.31 | 23.75 | 20.75 |
| 125 | 19.43 | 22.34 | 33.86 | 30.9 | 21.8 | 18.8 |
| 200 | 18.00 | 28.97 | 30.80 | 27.8 | 17.7 | 14.7 |
| 250 | 17.32 | 32.84 | 29.35 | 26.3 | 15.8 | 12.8 |

| Mechanical Characteristic | Product Standard | ||||||
| Testing Object | Jacket Material | Rated Temperature(℃) | 90/-55 | ||||
| Testing Material | PE | YD/T1019-2001 | Meet | ||||
| Aging Condition(℃*hrs) | 115*168 | UL/C(UL)/ETL | |||||
| Before Aging | Tensile Strength(Mpa) | >=16.5 | ANSI/EIA568C.2 | ||||
| Elongation(%) | >=300 | ISO/IEC 11801 | |||||
| After Aging | Tensile Strength(Mpa) | >=85% of unaged | Packaging | 305M/Box/Reel | |||
| Elongation(%) | >=50% of unaged | Printing | According to the customer's requirement | ||||
| Cold Bending(-20±2℃*4hrs) | No crack | ||||||
What are Cat6 Cables Used for?
Predominantly, CAT6 cables, a staple in the repertoire of CAT6 UTP cable manufacturers, are employed for establishing connections between computers and network devices such as hubs, routers, or switches. This setup is pivotal for enabling the distribution of files throughout a network or for securing internet connectivity.
Further, the versatility of CAT6 cables extends to linking computers with various peripheral devices, including printers and scanners. They also serve an essential function in managing both the inflow and outflow of LAN connections on patch panels.
In the sphere of local area networks (LAN), CAT6 Ethernet cables are integral for connecting a wide array of devices that require internet access. This encompasses a diverse range of equipment, from standard computing devices like desktops and laptops to modern televisions and the myriad components constituting the Internet of Things (IoT).
Regarding network compatibility, CAT6 cables are adept at supporting multiple forms of high-speed Ethernet networks. This includes standards such as 10BaseT, 100Base-TX, 1000 Base-T, and 10 GBase-T, each representing different categories of advanced Ethernet networking.
Related Products

CAT6 wire SFTP LAN cable
1000FT CAT6 SFTP shielded ethernet LAN cable outdoor cable manufacturer in China

CAT6 wire FTP LAN cable
200FT CAT6 FTP cable shielded ethernet network LAN cable manufacturer in China

CAT6A wire SFTP LAN cable
1000FT CAT6A SFTP shielded ethernet network cable network cable lan cable manufacturer ...

CAT5 CAT5E wire outdoor LAN cable
Outdoor CAT5 Cable 100FT 1000FT Outdoor Rated CAT5E waterproof Ethernet Cable direct ...