Tracer Wire high strength CCS Wire Copper Clad Steel Wire
Download CCS Tracer Wire Specification
12 GA High Strength Tracer Wire
High Strength Tracer Wire CCS 12 GA 1230 1245
14 GA High Strength Tracer Wire
High Strength Tracer Wire CCS 14 GA 1430 1445
10 GA High Strength Tracer Wire
High Strength Tracer Wire Manufacturer CCS 10 GA 1030 1045
What is the purpose of tracer wire?
Detecting the location of underground pipelines
tracer wire is mainly used to detect the location of underground pipelines. It is a detectable wire, easy to construct, and can be buried simultaneously with the pipeline. It is buried underground and in the middle of the pipeline, and is used to accurately locate the pipeline position during future excavation and repair, or to inform third parties in advance to avoid major accidents caused by damage
There are various forms of tracer wires, including tracer probes, tracer wire, and tracer warning tapes. Tracer probe is a miniature magnetic dipole emitting coil used to locate non-metallic pipelines with entrances and exits. There are two situations for tracer wire: one is to lay insulated metal wires along non-metallic pipelines during the laying process; Another method is to insert an insulated metal wire inside non-metallic pipelines with entrances and exits. Tracer warning tape is a type of warning tape with metal wires installed along high-risk buried pipelines, used to locate underground pipelines.
In practical applications, tracer wire is widely used in various gas and liquid pipeline transportation systems such as buried gas pipelines, oil pipelines, and urban water supply and drainage. Especially in complex urban pipeline construction sites, road construction sites, and building construction sites, tracer wire can effectively avoid huge property and economic losses caused by accidental damage.
why do tracer wire need to have high tensile requirements:
Ensure the physical strength of the wire body: Tracer wire need to withstand a certain amount of tension during installation and use, especially during non excavation laying. Tracer wire need to be pulled underground along with the pipeline, so they must have a certain tensile strength to prevent breakage during construction
Adapt to various construction environments: tracer wire may encounter complex geological and environmental conditions during use, such as rocks, sand, etc., which place higher demands on the physical properties of tracer wire. Tensile strength is an important indicator to measure whether the tracer wire can work stably in these environments
Extended service life: Tracer wire with higher tensile strength is less likely to break during use, thereby extending their service life and reducing additional costs and construction troubles caused by frequent replacement of tracer wires
The tensile requirements of tracer wires are usually met through the following methods:
Material selection: Tracer wires usually use copper-clad steel wire core and PE outer protective layer structure. Copper clad steel wire core provides good conductivity and certain tensile strength, while PE outer protective layer provides insulation, anti-corrosion, waterproof and anti-aging properties
Structural design: The structural design of the tracer wire also considers tensile requirements, such as increasing the diameter of the steel core or using a multi-layer structure to enhance its tensile performance
Application scenarios and importance of tracer wire:
tracer wire are mainly used for locating and detecting underground pipelines, especially in the installation and maintenance of gas PE pipelines. Due to the non-conductive nature of PE pipelines, metal detection equipment cannot be used for positioning, making tracer wire an important auxiliary tool. tracer wire with good tensile properties can ensure stable operation in various construction environments, improve construction efficiency and pipeline safety
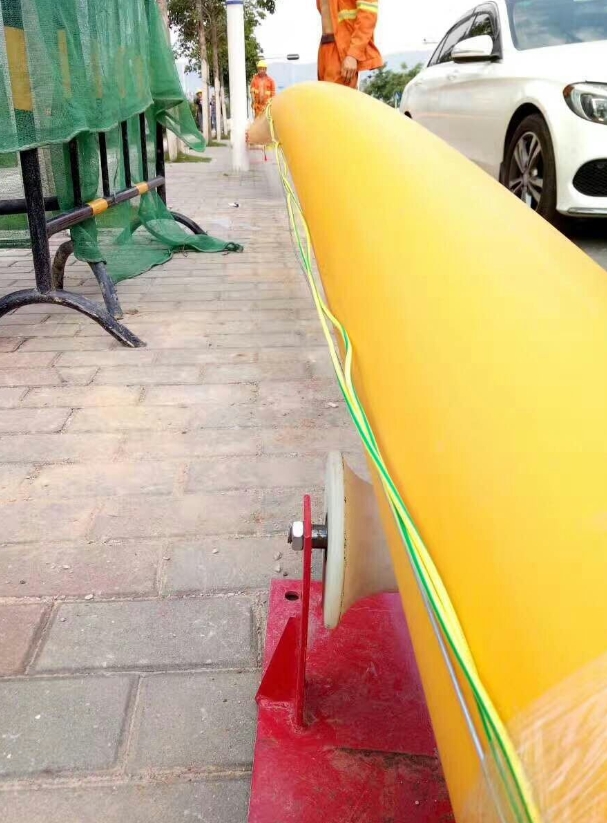

Why do buried communication cables need tracer wires?
The main reason for using tracer wire in buried network cables is to facilitate tracking and maintenance. Due to the non-conductive and non-magnetic nature of PE pipes, it is impossible to locate their specific location through traditional tracking methods, which has caused inconvenience for future pipeline maintenance. Therefore, tracer wire emerged and are usually laid together with PE pipes
The main functions of tracer wire include:
Easy to track: tracer wire generally use metal wire cores, and signals are applied through detection equipment. After the receiver receives the signal, it can accurately find the position of the tracer wire, thereby synchronously tracking the specific location of the PE pipeline, which is convenient for the modification and maintenance of the PE pipeline
Improve construction efficiency: During the construction process, tracer wire can help construction personnel accurately locate the position of pipelines, reduce the risk of accidental excavation and damage to pipelines, and improve construction efficiency
The commonly used tracer wire materials in the current market include:
Copper clad steel tracer wire: with good conductivity and magnetism, suitable for tracking buried pipelines
Thin film steel wire pressed tracer wire: providing stable signal transmission through the combination of thin film and steel wire
Wire tracing wire: using the conductivity of wires to track through current signals
The selection of materials for these tracer wire depends on the specific usage environment and requirements to ensure effective operation in various underground environments.
Common Tracer Wire Specifications
| Specification | Details |
| Wire Construction | Copper-Clad Steel (CCS) |
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Typically 12 AWG, 10 AWG, 14 AWG, or 18 AWG |
| Conductor Material | Steel core with copper cladding |
| Copper Cladding (%) | Typically 5% to 10% copper by weight (varies by manufacturer) |
| Insulation Material | Polyethylene (PE), High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), or PVC |
| Insulation Thickness | 0.030 to 0.080 inches (depending on application) |
| Max Operating Temperature | 75°C to 90°C (depending on insulation material) |
| Tensile Strength | Typically 250 lbs to 600 lbs (depending on wire gauge) |
| Voltage Rating | Typically rated for up to 600V (depending on insulation) |
| Color Options | Commonly yellow, orange, or blue for visibility and safety |
| Coil Length | Typically 500 ft, 1000 ft, or custom lengths available |
| Resistance | Varies by gauge; for example, 12 AWG CCS wire typically has 5.211 ohms per 1000 feet |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent due to copper cladding |
| UV Resistance | UV-resistant versions available for above-ground applications |
| Application | Utility locating, water, gas, sewer, and telecommunications |
1430 14GA tracer wire
| #14 CCS High Carbon Steel 21% Conductivity | CCS Conductor |
| Conductor Size | 14 AWG |
| Conductor Type | Copper-Clad Steel (CCS) |
| Temper | Dead Soft Annealed (DSA) |
| Average Break Load | 194 lbs |
| Minimum Tensile Strength | 48,000 psi |
| Minimum Elongation | 10% |
| Nominal Copper Thickness (% of Diameter) | 3% |
| Nominal Copper Weight | 13% |
| Nominal DC Resistance (ohms/1000 ft.) | 12.027 |
1230 12GA tracer wire
| #12 CCS High Carbon Steel 21% Conductivity | CCS Conductor |
| Conductor Size | 12 AWG |
| Conductor Type | Copper-Clad Steel (CCS) |
| Temper | Dead Soft Annealed (DSA) |
| Average Break Load | 302 lbs |
| Minimum Tensile Strength | 48,000 psi |
| Minimum Elongation | 10% |
| Nominal Copper Thickness (% of Diameter) | 3% |
| Nominal Copper Weight | 13% |
| Nominal DC Resistance (ohms/1000 ft.) | 7.564 |
1030 10GA tracer wire
| #10 CCS High Carbon Steel 21% Conductivity | CCS Conductor |
| Conductor Size | 10 AWG |
| Conductor Type | Copper-Clad Steel (CCS) |
| Temper | Dead Soft Annealed (DSA) |
| Average Break Load | 513 lbs |
| Minimum Tensile Strength | 48,000 psi |
| Minimum Elongation | 10% |
| Nominal Copper Thickness (% of Diameter) | 3% |
| Nominal Copper Weight | 13% |
| Nominal DC Resistance (ohms/1000 ft.) | 4.756 |
Application areas of tracer wire
Gas, water supply and drainage, oil transportation, electricity, industry, public facilities
tracer wire are mainly used in the following fields:
In the gas field, tracer wire are commonly used for detecting, tracking, and locating PE gas pipelines. By applying signals to the metal wire core through detection equipment and receiving the signals through a detection receiver, the accurate position of the tracer wire can be found, and the specific location of the PE gas pipeline can be determined for pipeline modification and maintenance
In the fields of water supply, drainage, and oil transportation, tracer wire are also widely used for detecting and locating water supply, drainage, and oil pipelines, helping to determine the location of underground pipelines and ensuring the smooth progress of construction and maintenance work
In the field of electricity, tracer wire also play an important role in the detection of power pipelines, helping to locate and identify buried power lines, ensuring the safety and maintenance of power facilities
In the field of industrial and public facilities: tracer wire are also used for the positioning of pipelines and cables in industrial and public facilities, ensuring the accurate location of various underground facilities and facilitating maintenance and management
Basic principles and usage methods of tracer wire:
tracer wire are usually laid together with pipelines and use metal wire cores. By applying a signal to the metal wire through a detection device and receiving the signal through a detection receiver, the accurate position of the tracer wire can be found, thereby determining the specific location of the pipeline. This method is suitable for locating and detecting various underground pipelines




