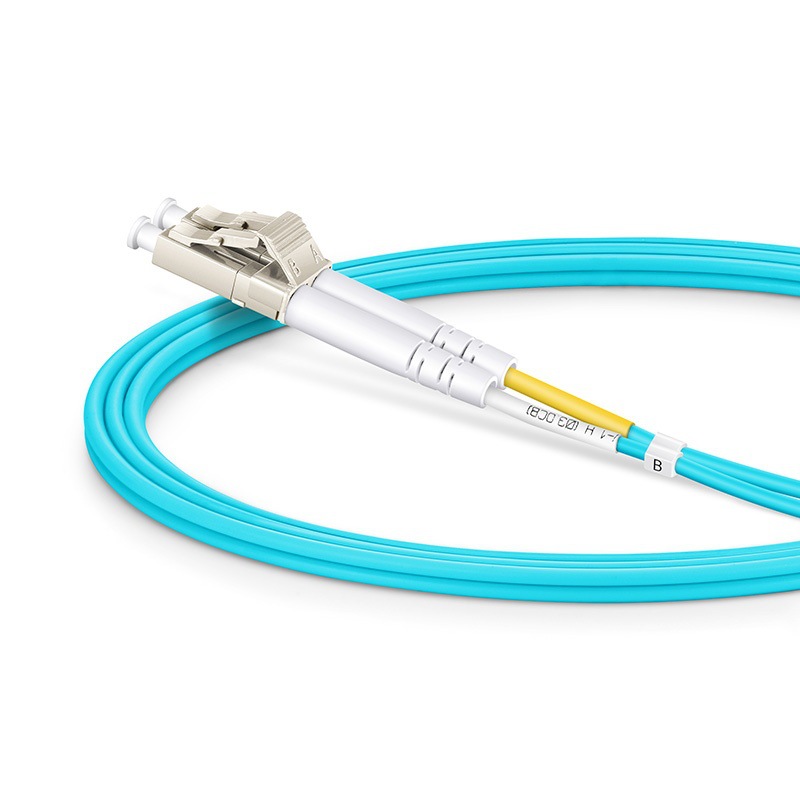
OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cable
OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cable
Item Number:OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cable
- Model: OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cord
- Size: OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4
- Color: White/Blue/Black/Gray/Custom
- Insulation: PE/PVC/Custom
- Shield: Unshielded/Custom
- Jacket: PVC/FR-PVC/LSOH/Custom
- Packing: Custom
- OD: Custom
- Conductor Material: Fiber
- Drain wire: None/Custom
Environmental Specifications:
Environmental Space – Non-plenum
Flame Test Method – CMR
Installation Temperature – 0 °C to +60 °C (+32 °F to +140 °F)
Operating Temperature – -20 °C to +60 °C (-4 °F to +140 °F)
General Specifications:
Cable Type
OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cord
Pairs, quantity
Custom
Cable Component Type
Horizontal/PVC/PE/Custom
Conductor Gauge, singles
Custom
Conductor Type, singles
Stranded
Characteristics:
- The transmission speed is very fast. Compared to other types of network cables, the transmission speed of the Super Five network cables will be faster, reaching 10 Mbps.
- The manufacturing process is also very good, which can effectively reduce signal interference. Moreover, they are all made of copper wires twisted together, so the electrical conductivity is very good.
- There are many brands sold on the market, so everyone must choose a large brand to ensure the quality of the network cable.
- Suitable for indoor applications
In general, the OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 optical fiber patch cord has several advantages, such as well overall performance, high-cost performance, and relatively low difficulty in construction and maintenance. Choosing it will not disappoint you.
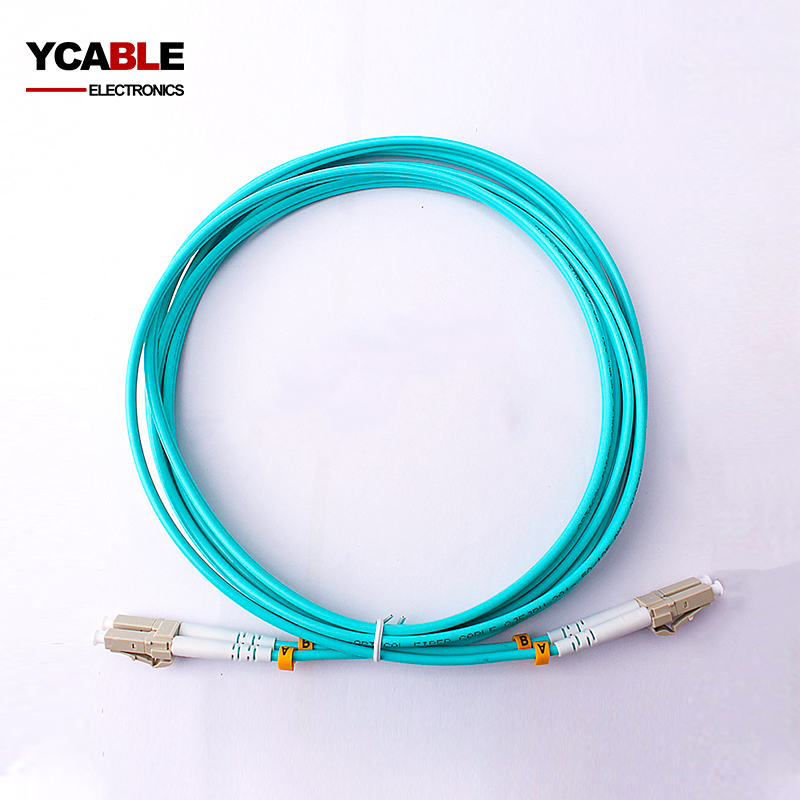


Categories
OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cord
| Electrical Specifications | |
| ANSI/TIA Category | OM1 OM2 OM3 OM4 Optical Fiber Patch Cord |
| dc Resistance Unbalance, maximum | 5 % |
| dc Resistance, maximum | 9.38 ohms/100 m |
| Mutual Capacitance | 5.6 nF/100 m @ 1 kHz |
| Nominal Velocity of Propagation (NVP) | 69 % |
| Operating Frequency, maximum | 200 MHz |
| Operating Voltage, maximum | 80 V |
| Transmission Standards | ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 CENELEC EN 50288-3-1 ISO/IEC 11801 Class D |
| Dielectric Strength, minimum | 1500 Vac 2500 Vdc |
Description
What is om1 om2 om3 and om4?
In the realm of optical networking, multimode and single-mode optical fiber cables represent two distinct pathways. Let’s unravel their intricacies, focusing on the multimode variety with its versatile optical fiber patch cord applications.
Multimode Fiber Cable: A Diverse Route
Multimode fiber cable, known for its larger core size, is adept at transmitting multiple light signals over shorter distances. This attribute makes it a robust choice for various network environments including local area networks (LANs), storage area networks (SANs), central offices, and data centers. These cables offer a blend of flexibility, reliability, and cost-efficiency.

The Spectrum of Multimode: OM1 to OM4
Unlike single-mode fibers, multimode fibers are broadly categorized into four types: OM1, OM2, OM3, and OM4, as per the ISO/IEC 11801 international standard. “OM” stands for optical multimode, and each type comes with distinct core sizes, bandwidths, data rates, and transmission distances.
- OM1 Multimode Fiber: Traditional 62.5/125μm fiber, known as OM1, is tailored for gigabit transmission rates with a bandwidth of 200/500MHZ*km @850/1300nm.
- OM2 Multimode Fiber: Sporting a 50/125μm specification, OM2 offers a larger bandwidth than OM1, particularly beneficial for 1gb/s systems, thanks to its compatibility with low-cost 850nm vcsel light sources.
- OM3 Multimode Fiber: Designed for 10G transmission, OM3 uses a 50um core and is optimized for 850nm VCSELs, supporting distances up to 300m in 10Gb/s Ethernet environments. It caters to a wide range of applications, from indoor to indoor/outdoor versatility.
- OM4 Multimode Fiber: Excelling in high bandwidth transmission, OM4 is often the choice for backbone networks in data centers and buildings. It supports longer transmission distances than OM3, making it ideal for 40G/100G applications.
Light Source Adaptation: LED vs. LD
While OM1 and OM2 multimode fibers traditionally utilize LED light sources, OM3 and OM4 are tailored for Laser Diode (LD) transmissions, marking a shift in light source optimization.
Application Scenarios
- OM1 and OM2: Predominantly used in short-haul networks, LANs, and private networks, these fibers are versatile in standard networking environments.
- OM3: Suited for larger private networks, OM3 steps up in scale and performance.
- OM4: Positioned at the forefront of network technology, OM4 is the go-to choice for high-speed, high-capacity networks found in data centers, financial centers, and corporate campuses.
In summary, the world of optical fiber patch cords is vast and varied, with multimode fibers like OM1, OM2, OM3, and OM4 serving different yet crucial roles in the optical networking landscape, each distinguished by its core size, bandwidth, and suitability for specific applications.
Optical Fiber Inquiries for Business Networks
Query on Optical Fiber in Passive Optical LANs
Does the optical fiber in passive optical LANs necessitate specific attributes? In such networks, each Optical Network Terminal (ONT) needs a single-mode fiber strand. For connections, SC/APC angle polish connectors are standard. If your infrastructure already includes single-mode fiber, your system is partially compatible.
Fiber Type in Passive Optical LAN (POL)
Does POL favor multimode or single-mode fiber? POL systems predominantly employ single-mode fiber, owing to its high capacity and long-distance support (up to 20 km). The network infrastructure comprises a single-mode fiber channel extending to desktops, linked via an optical splitter to a thin-client or ONT. Recently, converters blending single-mode and multimode fibers have emerged, facilitating the integration of existing multimode fibers in buildings and campuses.
Fiber Choice for 200-400 Gig Circuits
What fiber is optimal for 200-400 Gig circuits? Typically, OM4 or OM5 multimode fibers are suitable, with single-mode as an alternative. OM5 is tailored for short wave division multiplexing (SWDM), offering a cost-efficient choice for varying distances.
Explanation of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Technology
What constitutes Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) Technology? WDM technology enables multiple wavelengths (usually 2 or 4) over a single fiber. The IEEE 802.3bs Task Force, in 2016, integrated 200 Gb/s capability, endorsing up to 2 km support with SMF (4l WDM duplex fiber) and 10 km with SMF (4l WDM duplex fiber).
Fiber Recommendation for Data Centers
Which fiber type is advisable for data centers? To meet high bandwidth requirements, most data centers install OM4 or higher, like laser-optimized multimode fiber. Although single-mode fiber is an option, it necessitates pricier optics. OM5, a wide bandwidth multimode fiber, is emerging as a favorable choice, supporting multiple light wavelengths and cost-effective multimode optics.
Overview of Wide Band Multimode Fiber (WBMMF)
What is WBMMF and its application? WBMMF, or OM5 multimode fiber, is a recent development in fiber technology, optimized for Short Wavelength Division Multiplexing (SWDM). It supports 100 Gb/s transmission across four wavelengths (850 nm to 953 nm) using multimode optics, primarily designed for data center usage.
Singlemode vs. Multimode Fiber for Network Installation
Should networks opt for singlemode or multimode fiber? While singlemode fiber offers high bandwidth, multimode fiber, particularly OM4 and OM5, remains a favored choice in enterprise settings. These newer multimode fibers can handle most applications across required distances, and their optics are more cost-effective than singlemode optics.