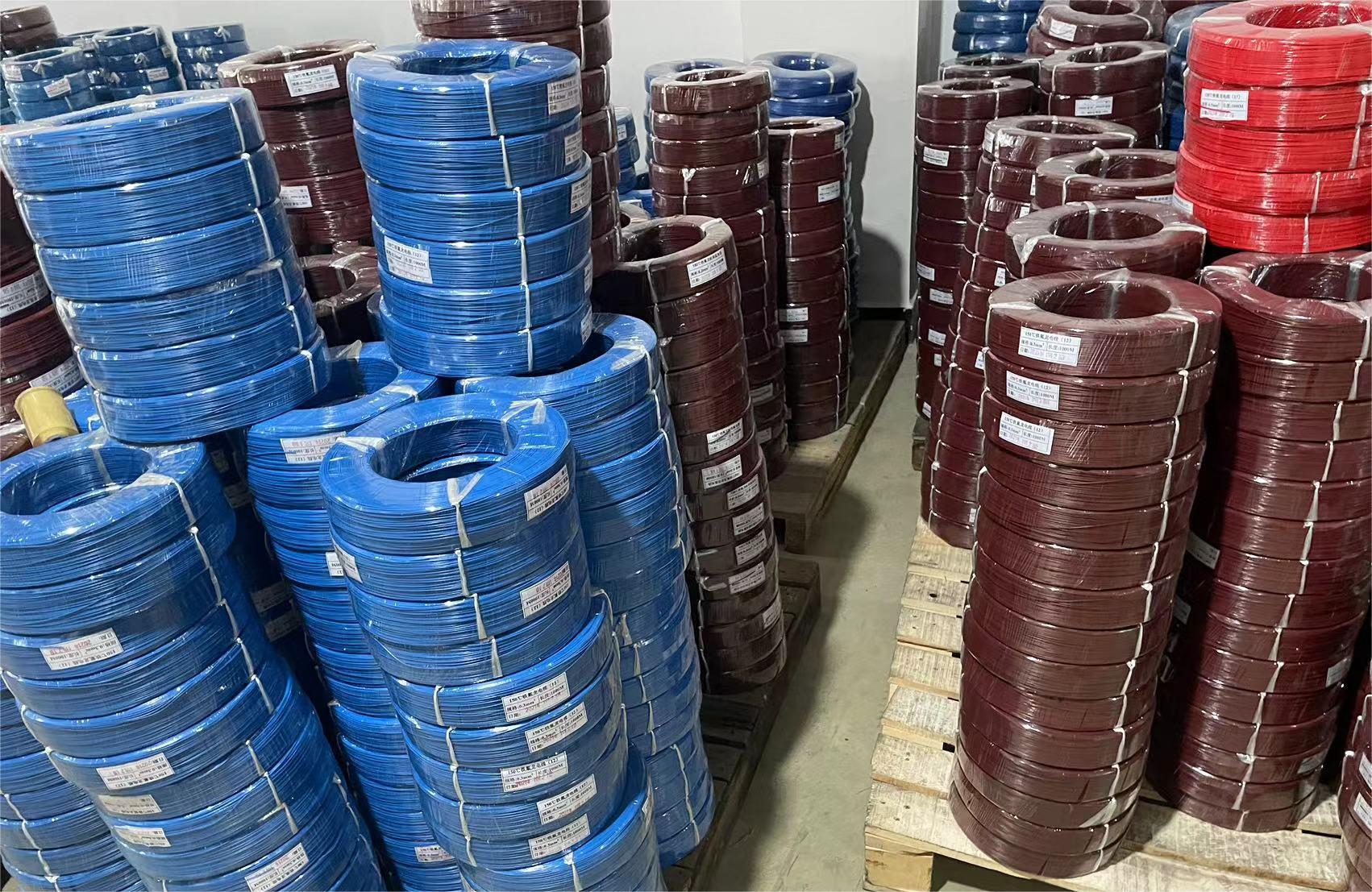
High Temperature Teflon Wire
High Temperature Teflon Wire
Item Number:High Temperature Teflon Wire
- Model: High Temperature Teflon Wire
- Size: 0AWG-36AWG
- Color: White/Blue/Black/Gray/Custom
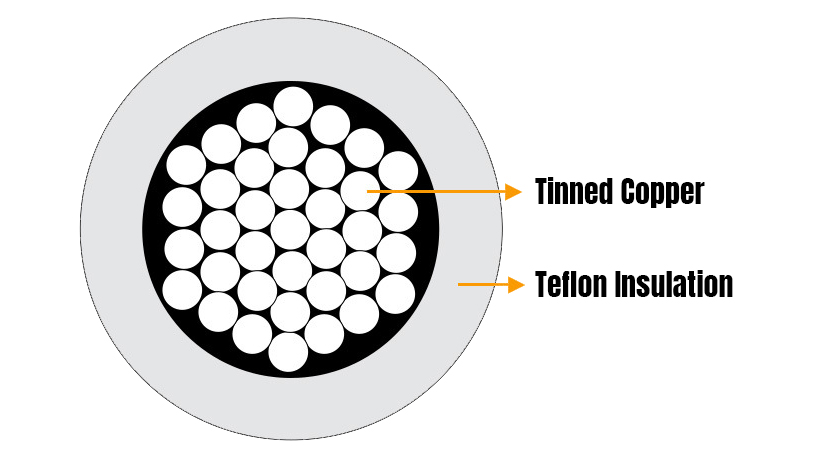
- Insulation: Teflon(PTFE, FEP, ETFE, PFA, MFA)
- Shield: Unshielded
- Jacket: None
- Packing: 100M, 305M, 610M and OEM
- OD: -
- Conductor Material: Bare Copper, Tinned copper, Silver plated copper
- Drain wire: None
Environmental Specifications:
Environmental Space – Non-plenum
Flame Test Method – VW-1 FT-2
Installation Temperature – -40 °C to +250 °C
Operating Temperature – -40 °C to +250 °C
Temperature Rating – 200 °C / 250 °C
General Specifications:
Cable Type
High temperature Teflon wire
Cable Component Type
Horizontal
Conductor Gauge, singles
0AWG-36AWG
Conductor Type, singles
Solid/Stranded Single Core Wire
Characteristics:
- High temperature Tefon products:
- Temperature resistance 150/200/250 degrees
- Oil resistance, acid, and alkali resistance
- Virtually eliminates skin irritation
- Color stable at elevated temperatures
- Suitable for UV, ozone, or moisture exposure
- Suited for liquid-immersed/High temperature applications
- Suitable for applications to -40°C~250°C
Teflon wire is a very good high temperature wire, Teflon material is very stable, It can be used in many harsh environments for a long time, and the wire made of Teflon is thinner than the high temperature wire made of other materials.
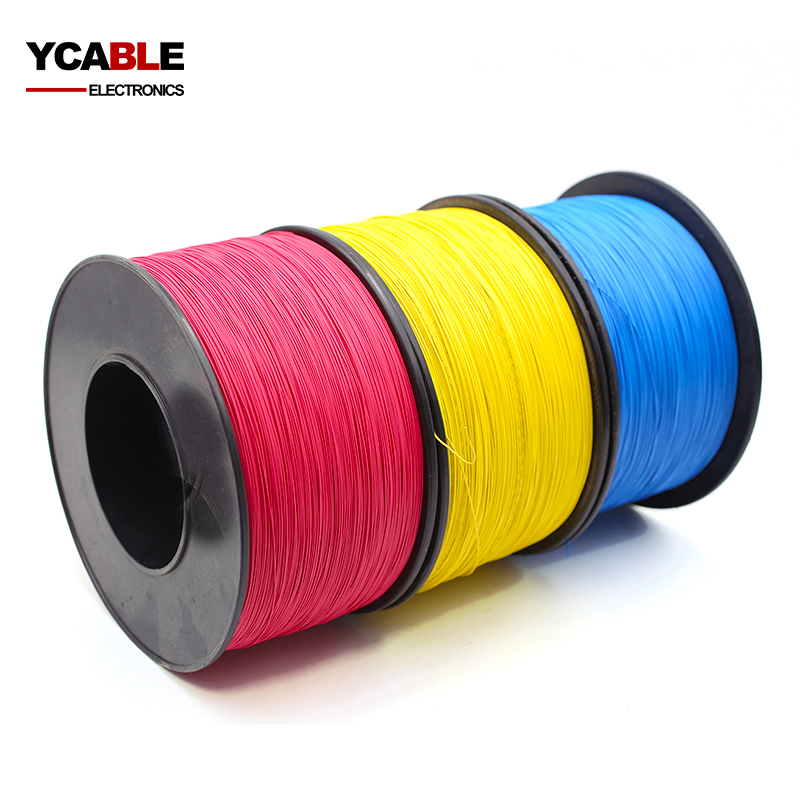


Categories
High Temperature Teflon Wire
| Teflon Wire Specifications | |||||
| AWG | Conductor structure number/wire diameter(mm) | Insulation thickness (mm) | Average outer diameter(mm) | Conductor DC resistance at 20 ℃ (Ω/km) | Package length (m) |
| 10 | 37 × 0.43 | 0.33 | 3.67 | 3.546 | 305 |
| 12 | 19 × 0.49 | 0.33 | 3.11 | 5.64 | 305 |
| 14 | 19 × 0.37 | 0.33 | 2.51 | 8.96 | 305 |
| 16 | 19 × 0.30 | 0.33 | 2.16 | 14.6 | 305 |
| 17 | 19 × 0.26 | 0.33 | 1.96 | 18.3 | 305 |
| 18 | 19 × 0.23 | 0.33 | 1.81 | 23.2 | 305 |
| 20 | 19 × 0.20 | 0.33 | 1.61 | 36.7 | 305 |
| 20 | 1 × 0.80 | 0.33 | 1.46 | 35.2 | 305 |
| 22 | 19 × 0.16 | 0.33 | 1.46 | 59.4 | 610 |
| 22 | 1 × 0.65 | 0.33 | 1.31 | 56.4 | 610 |
| 24 | 7 × 0.20 | 0.33 | 1.26 | 94.2 | 610 |
| 24 | 1 × 0.50 | 0.33 | 1.16 | 89.3 | 610 |
| 26 | 7 × 0.16 | 0.33 | 1.14 | 150 | 610 |
| 26 | 1 × 0.40 | 0.33 | 1.06 | 143 | 610 |
| 28 | 7 × 0.12 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 239 | 610 |
| 28 | 1 × 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 227 | 610 |
| 30 | 7 × 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.96 | 381 | 610 |
| 30 | 1 × 0.254 | 0.33 | 0.914 | 361 | 610 |
Description
What is Teflon wire used for?
Teflon Wire: The Core of Advanced Electrical Solutions
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), widely recognized as Teflon, transcends its common association with cookware to play a pivotal role in advanced wiring applications. Exploring the versatile world of Teflon coated and insulated wires unveils their critical importance.
Key Traits of Teflon Wires
- Thermal Endurance: Teflon wires excel in temperatures from -65°C to 260°C, much like desert dwellers adapting to harsh climates.
- Chemical Fortitude: Remarkably resistant to a wide array of chemicals, solvents, and oils.
- Non-Stick Quality: Teflon's inherent non-stick nature means less accumulation of contaminants.
- Electrical Resilience: Exhibits high resistance to electric currents, ideal for high-frequency electrical tasks.
Diverse Applications
- Industrial & Automation Settings
- Chemical Plants: Teflon wiring thrives in environments with corrosive chemicals.
- Temperature Monitoring: Ideal for devices like thermocouples due to their thermal resilience.
Aerospace & Defense Industries
- Aircraft Systems: Favoured for their lightweight nature and resistance to extreme conditions.
- Military Hardware: Reliability in rugged conditions makes Teflon wires a preferred choice.
Medical Field
- Medical Instruments: Suitable for sterilization at high temperatures and exposure to chemicals.
Electronics & Communication
- RF Communications: Teflon's suitability for high-frequency applications extends to radio-frequency systems.
- Computing & Networking: Used where high data transfer rates and minimal signal interference are essential.
Automotive Industry
- Engine Management: Vital in high-temperature engine environments.
Specialized Teflon Wire Variants
- Coaxial Cables: Essential for transmitting high-frequency signals with reduced interference.
- Multi-conductor Cables: Employed in scenarios necessitating multiple signal or power pathways.
Safety Aspects
- Fire Resistance: Teflon wires are inherently flame-retardant, enhancing safety in diverse applications.
- Low Smoke Emission: In fire scenarios, Teflon wires produce minimal smoke, mitigating hazards.
In the intricate domain of electrical engineering, Teflon wires serve as a versatile and resilient component, proving indispensable from aircraft systems to medical devices. Their adaptability and durability make them a cornerstone in the B2B electronics sector and beyond. Teflon wire, thus, stands as a reliable ally in challenging electrical applications, ready to be the solution when faced with demanding situations.
What is the difference between silicone and Teflon?
Silicone and Teflon—two heavyweights in the world of materials, each with its distinct set of properties. In the blue corner, we have silicone, famed for its flexibility and biocompatibility. In the red corner stands Teflon, renowned for its temperature resilience and chemical resistance. Let’s jump into the ring for a head-to-head comparison, shall we?
Basic Introduction
- Silicone: It is a synthetic polymer made up of silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. It's known for its flexibility and rubber-like texture.
- Teflon (PTFE wire): Teflon is the brand name for Polytetrafluoroethylene, a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene. It's recognized for its non-stick properties and chemical resistance.
Physical Properties
Silicone(Silicone wire):
- Flexible and elastic.
- Retains its properties over a wide temperature range.
- Generally transparent or translucent.
Teflon (PTFE wire):
- Stiffer compared to silicone.
- Extremely high melting point.
- Usually opaque.
Temperature Resistance
- Silicone: Handles temperatures from -55°C to 300°C. It's both cold and heat resistant.
- Teflon (PTFE): Exceptional temperature resilience, typically from -200°C to 260°C, making it ideal for extreme conditions.
Chemical Resistance
- Silicone: Resistant to water and many chemicals, but certain solvents can degrade it.
- Teflon (PTFE): Remarkably resistant to most chemicals and solvents.
Applications
Silicone:
- Medical devices due to its biocompatibility.
- Kitchen tools because of its heat resistance.
- Seals and gaskets owing to its elasticity.
- Electrical insulation for certain wires.
Teflon (PTFE):
- Non-stick coatings for cookware.
- Electrical wire insulation, especially for high-frequency applications.
- Gaskets and seals for aggressive chemical environments.
- Lining for pipes in chemical industries.
Health and Safety
- Silicone: Generally considered non-reactive, non-toxic, and safe for medical and food applications.
- Teflon (PTFE): Safe when intact. However, overheating Teflon-coated pans can release fumes potentially harmful to birds and can cause flu-like symptoms in humans.
Environmental Impact
- Silicone: While it doesn’t degrade quickly, it's less harmful to the environment than plastics derived from petroleum.
- Teflon (PTFE): Producing Teflon involves certain environmental concerns, particularly with the release of Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a persistent environmental contaminant. However, many manufacturers have reduced or eliminated the use of PFOA in Teflon production.
Both silicone and Teflon have carved their niches in myriad applications, thanks to their unique sets of properties. While silicone's flexibility and safety make it popular in the medical and food industry, Teflon's unparalleled chemical resistance and non-stick attribute have cemented its role in cookware and industrial applications.
When choosing between the two for a B2B endeavor, it's crucial to weigh the specific requirements against the properties of each material. Knowledge, after all, is the key to unlocking optimal business solutions!

How to remove Teflon coating from wire?
Ah, Teflon coatings—resilient and durable, but sometimes you need to strip it away to expose the conductor beneath. Given its resistance to heat and chemicals, removing Teflon can be more challenging than other types of insulation. But with the right technique, it's no Herculean task. Here's how you go about it:
Safety First!
- Goggles: Protect your eyes from any stray fragments.
- Gloves: Use cut-resistant gloves to avoid injury.
- Ventilation: Ensure you're working in a well-ventilated area if using chemicals.
Mechanical Stripping
This method is ideal for thicker wires where precision is less of a concern.
Tools Needed:
- Wire Strippers: Opt for the ones specifically designed for Teflon wire, if possible.
Procedure:
- Measure: Determine how much insulation you need to remove.
- Adjust: Set your wire strippers to the wire gauge you're working with.
- Strip: Grip the Teflon insulation with the strippers and pull towards the wire's end. It may require more force than typical PVC wire.
Thermal Stripping
Given Teflon's high resistance to heat, this method requires a very high temperature.
Tools Needed:
- High-Temperature Thermal Strippers: These tools use heated blades to melt away the insulation.
Procedure:
- Heat: Power on the thermal stripper and allow it to reach the required temperature.
- Position: Insert the wire between the blades at the length where stripping is desired.
- Activate: Engage the blades. The heated blades will melt through the Teflon insulation.
- Remove: Pull away the loosened Teflon insulation to expose the conductor.
Given the nature of Teflon, always double-check for residue or remaining bits of insulation after stripping. Ensure that the wire's integrity hasn't been compromised during the process.
Remember, if the stripping needs to be precise or on a large scale, consider investing in specialized tools or services tailored for Teflon-insulated wires. Precision and patience are your best allies here. Happy stripping!

What is teflon coated cable?
In the vast galaxy of cables, Teflon-coated variants stand out like a luminous star, guiding tech aficionados through challenging terrains. Let's get acquainted with this marvel, shall we?
Definition
A Teflon-coated cable consists of conductive wires enveloped by an insulation layer made from Teflon. Teflon, scientifically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a synthetic fluoropolymer celebrated for its high-temperature resilience, chemical resistance, and excellent dielectric properties.
Distinctive Attributes
- Temperature Endurance: Can operate efficiently within a vast temperature spectrum, often from -65°C to 260°C.
- Chemical Inertness: Resists most chemicals and solvents, ensuring longevity even in corrosive environments.
- Electrical Excellence: Exceptional dielectric properties make Teflon cables ideal for minimizing signal loss, especially in high-frequency applications.
- Fire Resistant: Naturally flame-retardant, reducing fire hazards.
- Low Friction: Teflon’s smooth surface ensures minimal abrasion when pulling through conduits or tight spaces.
Applications in the B2B Landscape
Electronics and Communication
- RF Cables: The low dielectric constant and low signal loss of Teflon make it a preferred choice for radio-frequency applications.
- Advanced Computing: Used in high-speed data transfer scenarios where signal integrity is crucial.
Industrial
- Sensors and Probes: Especially those exposed to elevated temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
- Heating Equipment: Teflon's high-temperature resilience makes it apt for this application.
Aerospace and Defense
- Aircraft Systems: These systems often require cables that can endure extreme conditions, making Teflon-coated cables a go-to.
- Military Communications: Given the need for reliable and durable cabling.
Medical
- Medical Instruments: Instruments that undergo sterilization or are exposed to harsh chemicals benefit from Teflon's resilience.
Variants and Grades
- PTFE (Pure Teflon) Cables: Offer the highest temperature and chemical resistance.
- FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) Cables: Slightly different properties than PTFE but still provide superior insulation.
- PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) Cables: Combine attributes of PTFE and FEP, offering flexibility and durability.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
- Low Smoke Emission: In the unfortunate event of a fire, Teflon-coated cables emit lesser toxic fumes compared to many other materials.
- Environmental Concerns: Manufacturing Teflon traditionally involved the use of PFOA (Perfluorooctanoic acid), which is a concerning environmental pollutant. However, many producers have now phased out or minimized its use.
In the concert of cables, Teflon-coated ones hit the high notes of durability, reliability, and performance. Whether it's data zooming through a server farm or signals navigating an aircraft's intricate systems, these cables ensure the message always gets through.
For businesses seeking the creme de la creme of cabling solutions, the Teflon-coated option is a symphony of excellence worth tuning into!








