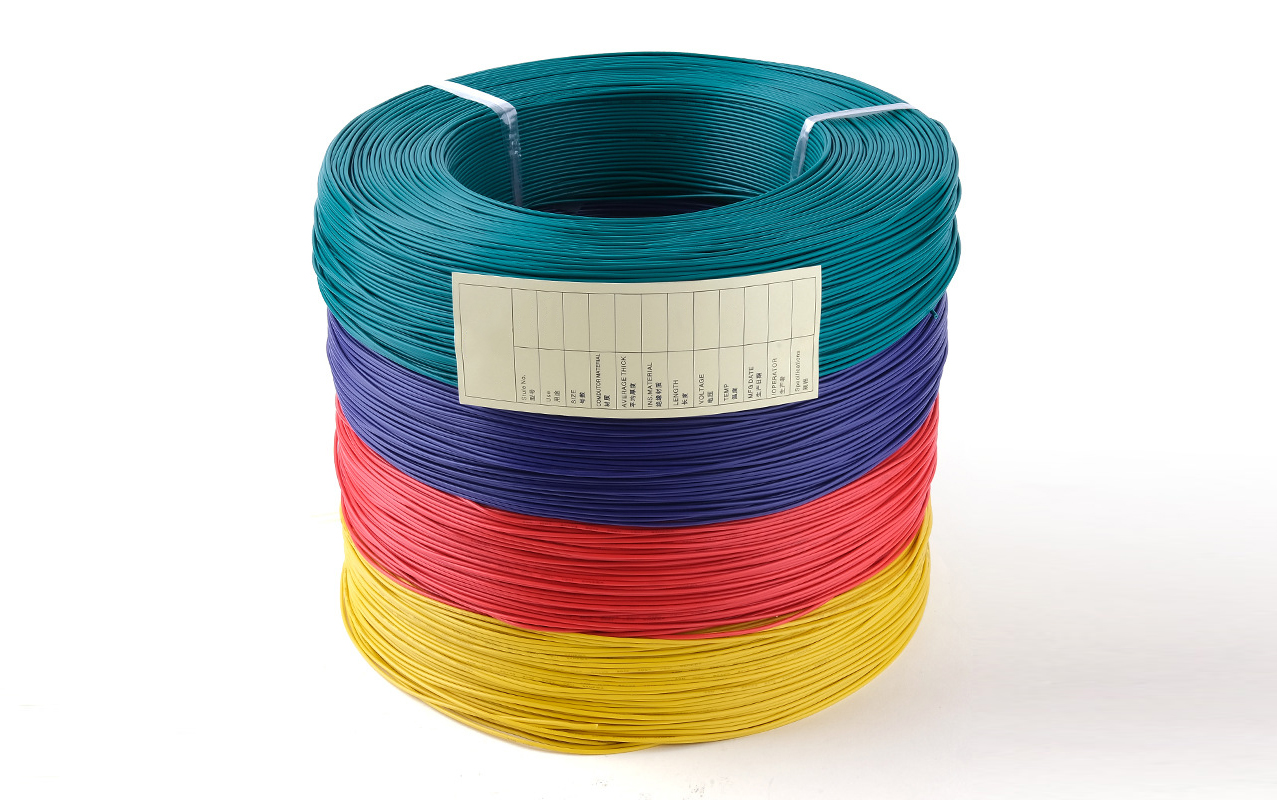
PFA wire
PFA wire
Item Number:PFA wire
- Model: High Temperature Teflon PFA wire
- Size: 0 GA-36 Gauge
- Color: Transparent, black, green, red, yellow, white, Custom
- Insulation: PFA 250℃
- Shield: None
- Jacket: PFA
- Packing: 305m, 610m, 2000, 4000m, Custom
- OD: According to the standard/Custom
- Conductor Material: Tinned copper, silver plated copper, bare copper
- Drain wire: None
Environmental Specifications:
Environmental Space – Non-plenum
Flame Test Method – VW-1 FT-2
Installation Temperature – -40 °C to +250 °C
Operating Temperature – -40 °C to +250 °C
Temperature Rating – 200 °C / 250 °C
General Specifications:
Cable Type
PFA Teflon wire
Cable Component Type
PFA
Conductor Gauge, singles
0AWG-36AWG
Conductor Type, singles
Solid/Stranded Single Core Wire
Characteristics:
- High temperature PFA Tefon products:
- Temperature resistance 250 degrees
- Oil resistance, acid, and alkali resistance
- Virtually eliminates skin irritation
- Color stable at elevated temperatures
- Suitable for UV, ozone, or moisture exposure
- Suited for liquid-immersed/High temperature applications
- Suitable for applications to -40°C~250°C
PFA wire is a very good high temperature Teflon wire, PFA Teflon material is very stable, It can be used in many harsh environments for a long time, and the wire made of PFA is thinner than the high temperature wire made of other materials.


Categories
High Temperature PFA Teflon Wire
| PFA Wire Specifications | |||||
| AWG | Conductor structure number/wire diameter(mm) | Insulation thickness (mm) | Average outer diameter(mm) | Conductor DC resistance at 20 ℃ (Ω/km) | Package length (m) |
| 10 | 37 × 0.43 | 0.33 | 3.67 | 3.546 | 305 |
| 12 | 19 × 0.49 | 0.33 | 3.11 | 5.64 | 305 |
| 14 | 19 × 0.37 | 0.33 | 2.51 | 8.96 | 305 |
| 16 | 19 × 0.30 | 0.33 | 2.16 | 14.6 | 305 |
| 17 | 19 × 0.26 | 0.33 | 1.96 | 18.3 | 305 |
| 18 | 19 × 0.23 | 0.33 | 1.81 | 23.2 | 305 |
| 20 | 19 × 0.20 | 0.33 | 1.61 | 36.7 | 305 |
| 20 | 1 × 0.80 | 0.33 | 1.46 | 35.2 | 305 |
| 22 | 19 × 0.16 | 0.33 | 1.46 | 59.4 | 610 |
| 22 | 1 × 0.65 | 0.33 | 1.31 | 56.4 | 610 |
| 24 | 7 × 0.20 | 0.33 | 1.26 | 94.2 | 610 |
| 24 | 1 × 0.50 | 0.33 | 1.16 | 89.3 | 610 |
| 26 | 7 × 0.16 | 0.33 | 1.14 | 150 | 610 |
| 26 | 1 × 0.40 | 0.33 | 1.06 | 143 | 610 |
| 28 | 7 × 0.12 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 239 | 610 |
| 28 | 1 × 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 227 | 610 |
| 30 | 7 × 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.96 | 381 | 610 |
| 30 | 1 × 0.254 | 0.33 | 0.914 | 361 | 610 |
Description
What is PFA wire?
Perfluoroalkoxy, commonly abbreviated as PFA, stands as a high-performing fluoropolymer. Renowned for its capability to endure temperatures up to 260°C, PFA emerges as an optimal material for high-temperature scenarios. Its chemical resistance is also notably exceptional. PFA insulated wire, regularly employed as a thermocouple wire, is prevalent in demanding military and aerospace settings. The versatility of PFA allows for its fabrication in both extruded and foamed forms.
Selecting PFA for insulation or jacketing on wires and cables is advantageous for multiple reasons:
- High-Temperature Mechanical Strength: PFA surpasses FEP insulation in mechanical strength, particularly at elevated temperatures, making PFA coated wire a robust option.
- Enhanced Operating Temperature: PFA offers a superior operational temperature range and maintains formidable mechanical integrity even under high heat, distinguishing itself from FEP insulation.
- Flexibility in Cold Conditions: PFA insulated wire retains its flexibility in lower temperatures, ideal for diverse applications.
- Broad Application Spectrum: From automotive oxygen and NOx sensors to challenging conditions in medical, scientific, computer, aircraft, and marine systems, PFA insulated wire proves its adaptability.
- Space Efficiency: Due to its low dielectric constant, PFA can be extruded with thinner walls. This property renders PFA coated wire factory products space-efficient, particularly in cable bundling or wiring harnesses, where space conservation is crucial.
- Installation Ease: The mechanical sturdiness of PFA, coupled with its low friction coefficient, facilitates easier installation of long wire lengths, enhancing operational efficiency.
As a material, PFA's molecular structure, characterized by strong Carbon-Oxygen-Fluorine bonds, endows it with properties akin to PTFE, making it a preferred choice for electrical cable sheathing. PFA sheathing excels in chemical resistance, tolerating extreme temperatures, strong mineral acids, lubricants, oils, and inorganic oxidizing agents. Additionally, its flexibility and heightened dielectric strength are advantageous. Notably, PFA's melt processability is superior to PTFE, attributed to its lower melt viscosity. However, it is reactive to fluorine and molten alkali metals.
PFA cables are indispensable in sectors like medical life sciences, military defense, and aviation. They are also ideal for environments experiencing intense lighting or extreme temperature variations. In summary, PFA wire, including Teflon wire and PFA coated wire from specialized factories, represents a multifaceted and efficient solution for a wide range of industrial applications.

Advantages of PFA wire
Extruded Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) insulated wire and cable share several advantages with FEP, yet stand out in certain aspects:
- Dielectric Strength: PFA insulated wire showcases remarkable dielectric strength, a step above what's typically seen in silicone rubber insulated wire, without inheriting its common drawbacks.
- Enhanced High-Temperature Performance: PFA wire offers an increased operating temperature range and boasts greater mechanical strength at these elevated temperatures compared to FEP insulation.
- Space Efficiency: When compared to silicone wire, PFA wire, cable assemblies, and bundles exhibit a much reduced diameter. This compactness significantly decreases the volume occupied and allows for a smaller bend radius, granting designers more freedom in space-constrained systems.
- Corona Inception Qualities: PFA insulated wire demonstrates commendable resistance to corona discharge initiation.
- Robust Durability: Exhibiting excellent resistance to degradation by dielectric/cooling fluids, PFA insulated wire ensures long-lasting durability.
- Chemical Inertness: This wire type remains unaffected by most industrial solvents and chemicals, maintaining its integrity in diverse environments.
- NASA Low Outgassing Standards Compliance: PFA insulated wires meet NASA’s stringent requirements for Total Mass Loss (TML) and Collected Volatile Condensable Materials (CVCM) levels.
- Resistance to Physical Damage: Unlike other materials, PFA insulated wire is less prone to issues like "pin-holing" and high voltage punch-through, which can occur due to abrasion or strand breakage during usage.
- Enhanced Contact Resistance: While avoiding contact with sharp edges is advisable in high voltage systems, PFA wires show increased resistance to damage from such encounters.
In summary, PFA wire, including pfa coated wire and Teflon wire, sourced from specialized pfa coated wire factories, delivers a combination of high performance and reliability, making it a suitable choice for various applications requiring high durability and efficient space utilization.

What is the difference between PFA wire and PTFE wire?
PFA, an acronym for Perfluoroalkoxy, is also widely recognized under DuPont’s brand name, Teflon® PFA. This polymer is celebrated for its low friction coefficient, contributing to its excellent non-stick qualities. PFA is a versatile and flexible material, boasting high resistance to stress cracking and nearly universal chemical and solvent resistance. It thrives under varied temperature conditions, enduring up to 260°C (500°F) and offering remarkable flame resistance, chemical stability, and high dielectric strength.
In industrial applications, PFA tubing is essential in critical, highly corrosive processes. It serves as a protective lining for chemical equipment against corrosion. Its use extends to filtration housings, heat exchangers, pump housings, fittings, and more. Process Technology incorporates PFA in various products, including TIH inline chemical heaters, Pulsar point-of-use (POU) inline heaters, XC Series inline exchangers, and X Series immersion coils.
PTFE, or Polytetrafluoroethylene, is another synthetic fluoropolymer, often known as Fluon or Syncolon and famously as Teflon. Discovered in 1938 by Roy Plunkett at DuPont, PTFE is a fluorocarbon solid composed of carbon and fluorine. It’s notably hydrophobic, resisting moisture absorption. Its low friction coefficient, owing to fluorine's high electronegativity, is responsible for its famed slipperiness. PTFE is characterized by high chemical resistance, temperature resilience, weathering resistance, and impressive electrical and thermal insulation properties.
PTFE’s uses are diverse, ranging from non-stick coatings in cookware to lining pipes, containers, and tanks for corrosive substances. Its inert nature makes it an excellent lubricant in machinery, minimizing energy consumption and wear. Process Technology employs PTFE in various equipment, including TIH and SHC inline chemical heaters, Lufran ultra-pure water heaters, HX Series immersion heaters, X Series immersion coils, and LTFH high-temperature filter housing.
The key differences between PFA and PTFE lie in their distinct properties. PFA's alkoxy substituents allow for conventional melt processing techniques like injection molding and screw extrusion, unlike PTFE. PFA is more flexible but with a lower flex-life, making it less suitable for repeated bending. PTFE, while slightly more heat-resistant, doesn't match PFA in flow, creep resistance, and thermal stability. Their melting points are 260°C for PFA and 327°C for PTFE. PFA is more prone to water absorption and weathering than PTFE but excels in salt spray resistance. Notably, PFA has a dielectric strength 3 to 4 times greater than that of PTFE.

Q: What is the temperature rating of PFA wire?
A: PFA insulation is capable of enduring temperatures as high as 260° Celsius, showcasing enhanced mechanical robustness at such elevated temperatures, especially when juxtaposed with FEP insulation. This attribute makes PFA insulated wire, including those produced by pfa coated wire factories, an ideal choice for applications demanding high-temperature resilience.
Q: Which is better PFA or PTFE?
A: PFA excels over PTFE in flexibility, especially in the realm of tubing applications, making it a preferred choice for such uses. However, when considering flex life, or the ability to withstand continuous bending, PFA doesn't quite match up to PTFE's endurance. On the heat resistance front, PTFE holds a slight edge over PFA, offering a bit more resilience in high-temperature environments. This distinction is particularly relevant in selecting materials like PFA wire, pfa coated wire, pfa insulated wire, Teflon wire, or sourcing from a pfa coated wire factory, where the balance of flexibility and heat resistance is crucial.
Custom PFA Insulated Wire and Cable Solutions
PFA Insulated Cable and Wire, renowned for their high-temperature application suitability, endure operating temperatures up to 260° Celsius, outperforming FEP insulation in mechanical strength under such conditions. These wires also demonstrate impressive toughness in low-temperature environments. In applications where a chemical-resistant wire and cable are essential, PFA insulated variants are preferred due to their inert nature against most industrial solvents and chemicals. The functional stability of PFA insulation is maintained across a broad temperature range, from –200° C to +260° C.
At YCABLE ELECTRONICS, we specialize in crafting custom PFA insulated wire and cable. Our manufacturing capabilities include both thin and heavy wall wire insulation, alongside cable jackets, tailored to the specific needs of your project. We offer a variety of dimensions, accommodating sizes from the delicate AWG 40 to the more substantial AWG 2/0. Catering to diverse application requirements, our minimum order quantity starts at 1000 ft, ensuring a flexible approach to both small and large-scale projects, all created with the precision and quality expected of a leading pfa coated wire factory.







